
What is an oxygen sensor?
- An oxygen sensor (or lambda sensor) is an electronic sensing device that is placed throughout a vehicles exhaust system to measures the proportion of oxygen (O2) in the gas being analysed. It was developed by Robert Bosch GmbH during the late 1960s under the supervision of Dr. Günter Bauman.
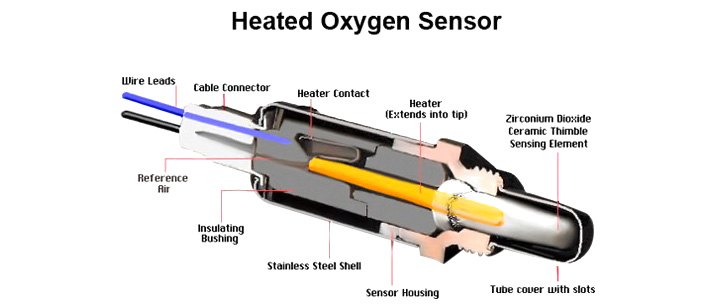
Inside an O2 Sensor
Common Symptoms
- A failed oxygen sensor (O2 or lambda sensor) may cause the vehicle to fail an emissions test. The failed sensor will cause a trouble code to be set and the Check Engine Light to illuminate.
- Oxygen sensors can fail if they are contaminated with oil, coolant, or silicone. If fluid contamination has caused an oxygen sensor failure, the source of the fluid must be resolved or the new sensor may be ruined.
Common Misdiagnoses
- There are many things can be traced back to a oxygen sensor trouble code, even if the sensor is working correctly.
- Simply changing one or all sensors for a oxygen sensor code may not help your issue.
- Maintenance and tune up issues can cause exhaust gas to read incorrectly causing a diagnostic trouble code (DTC).
- Exhaust leaks or unmetered air entering the exhaust system.
- Intake and exhaust leaks can trigger an oxygen sensor trouble code. Repairing the leak will resolve the problem.
- On vehicles 1996 and newer, using an inexpensive “universal” oxygen sensor will cause problems with the emissions system and is highly discouraged.

A newer version is available of this O2 Sensor

